今天的算法课上,老师讲了一个比较有意思的数据结构:Treap。它的名字就比较有意思,为什么叫Treap呢?是Tree + Heap两个单词的结合,所以这个数据结构也就是二叉树和二叉堆的结合了。
简介
Treap也是平衡二叉搜索树的一种。
Balanced Binary Search Tree 也可以简称为 Balanced Search Tree,为了方便区分我下面会简称为BBST。
我比较熟悉的一种BBST是红黑树,当然让我徒手去写一个红黑树,貌似还做不到呢(
在《算法 第四版》中详细介绍红黑树,当我知道《算法》这本的作者 Robert Sedgewick 教授就是红黑树的发明者时,只能说🐮🍺。 在coursera上听过 Robert Sedgewick 教授的课。讲到红黑树的时候,介绍自己是红黑树的作者只是一句话带过,丝毫没有一点吹嘘的感觉,真心佩服。
不过因为红黑树太复杂了,涉及节点颜色的反转,旋转。所以Treap就出现了,Treap的实现比较简单直观,速度也不错,很好的平衡了编码复杂度和时间效率。
简单的说,Treap 是一棵拥有键值、优先级两种权值的树。对于键值,它是一棵二叉搜索树;对于优先级,它是二叉堆。
每个节点的优先级是随机确定的,因此操作的时间复杂度也是随机的。不过可以证明插入,删除和查找的平均时间复杂度都为O(lgn)。而红黑树的时间复杂度也为O(lgn)。
实现
算法竞赛入门经典-训练指南这本书上,使用C++实现的Treap,这里我用Java实现和完善一波,把它改写成一个和TreeMap类似的数据结构,暂时把它叫做TreapMap。完整的代码在Gist上。
TreeMap是使用红黑树实现的键值对存储的数据结构,而我这里要实现的TreapMap是基于Treap实现的键值对存储数据结构。最后会对两者的性能进行比较。
Treap节点
Treap的节点定义如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
static class Node<K extends Comparable, V> implements Comparable<Node> {
Node[] children = new Node[2]; // left child, right child
int priority; //优先级
K key;
V value;
public Node(int priority, K k, V v) {
this.priority = priority;
this.key = k;
this.value = v;
children[0] = children[1] = null;
}
Node getLeftChild() {
return children[0];
}
Node getRightChild() {
return children[1];
}
int directionFor(K anotherKey) {
if (anotherKey == this.key || anotherKey.equals(this.key)) return -1;
// compareTo return negative integer when this object is less than another,
// that is another is greater then this, so it should be in right child(children[1])
return this.key.compareTo(anotherKey) < 0 ? 1 : 0;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Node another) {
return this.key.compareTo(another.key) < 0 ? 0 : 1;
}
}
|
模仿算法竞赛入门经典上的代码,采用数组来存放左右孩子。这样在比较key的时候,可以通过返回0或1,来确定是在左孩子还是右孩子,主要逻辑在directionFor方法中。我已经写了一些注释,为了方便这里的key必须实现Comparable接口,这样才能比较,比较的时候,如果当前对象比另一个对象小,compareTo返回小于0的数,也就是另一个对象比当前对象大,所以在当前对象的右孩子,即返回1。
旋转
当插入后,如果新节点违反了堆的性质,即子节点的优先级小于父节点(最大堆)。这时候,需要旋转一下来调整。也因为这样的旋转使得它成为一棵BBST,因为节点的优先级是随机生成的,通过旋转可以使得树更加平衡。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
/**
* d ^ 1 equals 1 -d, when d must be 1 or 0.
* So this method handles both left rotate and right rotate
*
* @param parent parent node to rotate
* @param d rotate direction
* @return parent node after rotate
*/
private Node rotate(Node parent, int d) {
if (d != 1 && d != 0) throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException();
Node k = parent.children[d ^ 1];
parent.children[d ^ 1] = k.children[d];
k.children[d] = parent;
parent = k;
return parent;
}
|
上面这个方法同时处理了左旋和右旋。你可以分别验证这两种情况,是完全没有问题的,书上的那一小段C++代码实在是妙啊。并且使用d ^ 1来取代1 - d来提高效率。旋转结束后,要返回旋转后的父节点,在调用者那里进行赋值,改变父节点的引用。比如插入的时候要这样做:
1
|
parent.children[d] = insert(parent.children[d], key, value);
|
如果不进行赋值,那么这个父节点还是没有改变的,因为Java的函数是传值的,这里就没有C/C++来的方便了。
插入
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
private Node<K, V> insert(Node parent, K key, V value) {
if (parent == null) {
parent = new Node<>(getRandomPriority(), key, value);
modeTime++;
} else {
int d = parent.directionFor(key);
// key重复,直接覆盖value
if (d == -1) {
parent.value = value;
} else {
parent.children[d] = insert(parent.children[d], key, value);
if (parent.children[d].priority > parent.priority) {
// 插入后,如果子节点的优先级大于父节点的优先级,进行旋转
parent = rotate(parent, d ^ 1);
modeTime++;
}
}
}
return parent;
}
|
上述代码使用递归实现,同样的每次递归都需要改变父节点的引用。当key重复时,我们直接覆盖原来的value;否则,根据键值大小选择左节点或右节点继续递归下去,直到叶子节点或者key重复为止。
TreapMap对外值提供一个put方法来插入元素:
1
2
3
4
5
|
public void put(K key, V value) {
int oldMod = modeTime;
root = insert(root, key, value);
if (oldMod != modeTime) size++;
}
|
删除
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
private Node<K, V> delete(Node parent, K key) {
V v = get(key);
// key not exists
if (v == null) {
return parent;
}
v = null;
int d = parent.directionFor(key);
if (d == -1) {
// 待删除的节点只有一个子节点或没有子节点
if (parent.getLeftChild() == null) {
parent = parent.getRightChild();
modeTime++;
} else if (parent.getRightChild() == null) {
parent = parent.getLeftChild();
modeTime++;
} else {
//待删除的节点有两个子节点,把优先级高的子节点旋转的父节点,再递归删除待删除的节点
//如果左节点的优先级高于右节点,右旋,接着在右子树中递归删除。
int d2 = parent.getLeftChild().compareTo(parent.getRightChild());
parent = rotate(parent, d2);
delete(parent.children[d2], key);
}
} else {
parent = delete(parent.children[d], key);
}
return parent;
}
|
上面的Java代码完善了书中的代码,在key不存在的时候直接返回。如果待删除的节点只有一个子节点或没有子节点,就比较方便,直接用改子节点替代待删除的节点即可;如果待删除的节点有两个子节点,情况就复杂了一点。先把优先级高的子节点旋转的父节点,再递归删除待删除的节点。
最后也是提供一个public的方法用于删除:
1
2
3
4
5
|
public void remove(K key) {
int oldMod = modeTime;
root = delete(root, key);
if (modeTime != oldMod) size--;
}
|
测试
分别对TreapMap和TreeMap进行插入和删除的测试,并且比较两者的性能:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
|
@org.junit.Test
public void testTreap() {
System.out.println("----------TreapMap test start----------");
TreapMap<Integer, String> treap = new TreapMap<>();
treap.put(1, "hello");
treap.put(2, "world");
System.out.println("treap[1] = " + treap.get(1));
long time = 0;
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < 1e6; i++) {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
treap.put(i, i + "test" + random.nextInt(Integer.MAX_VALUE));
if (i % 5 == 0) {
treap.remove(i);
}
time += (System.currentTimeMillis() - start);
}
System.out.println("size: " + treap.getSize());
System.out.println("treap[1] = " + treap.get(1));
System.out.println("TreapMap time: " + time);
System.out.println("----------TreapMap test end----------");
}
@org.junit.Test
public void testTreeMap() {
System.out.println("----------TreeMap test start----------");
TreeMap<Integer, String> treeMap = new TreeMap<>();
treeMap.put(1, "hello");
treeMap.put(2, "world");
System.out.println("treeMap[1] = " + treeMap.get(1));
Random random = new Random();
long time = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 1e6; i++) {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
treeMap.put(i, i + "test" + random.nextInt(Integer.MAX_VALUE));
if (i % 5 == 0) {
treeMap.remove(i);
}
time += (System.currentTimeMillis() - start);
}
System.out.println("size: " + treeMap.size());
System.out.println("treeMap[1] = " + treeMap.get(1));
System.out.println("TreeMap time: " + time);
System.out.println("----------TreeMap test end----------");
}
|
最终的结果TreapMap的速度比TreeMap的快两倍多。但是我发现一个TreapMap删除时候的🐛bug,这样即使速度再快没有正确性也没用。测试结果如下:
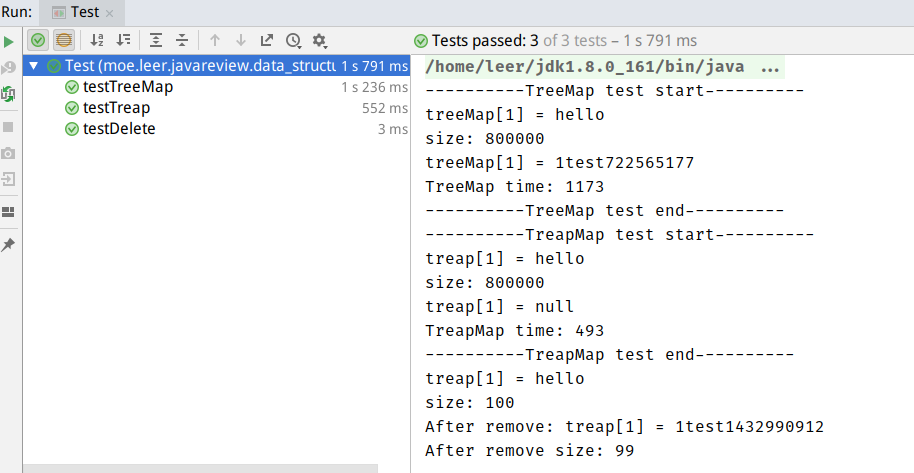
treapMap.get(1)的值是不应该为null的,但是结果确实null,目前我还没发现自己错在哪里(有哪位大佬发现了告诉我一声啊。完整的代码在Gist上可以看到。
参考
